In the face of accelerating climate change, we must explore innovative solutions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and safeguard our planet’s future. Carbon capture, a cutting-edge technology, offers a promising avenue for mitigating the impact of carbon dioxide (C02) emissions. By capturing and storing CO2 before it enters the atmosphere, this breakthrough process helps us make significant strides toward a cleaner and more sustainable future.
So, how does carbon capture work?
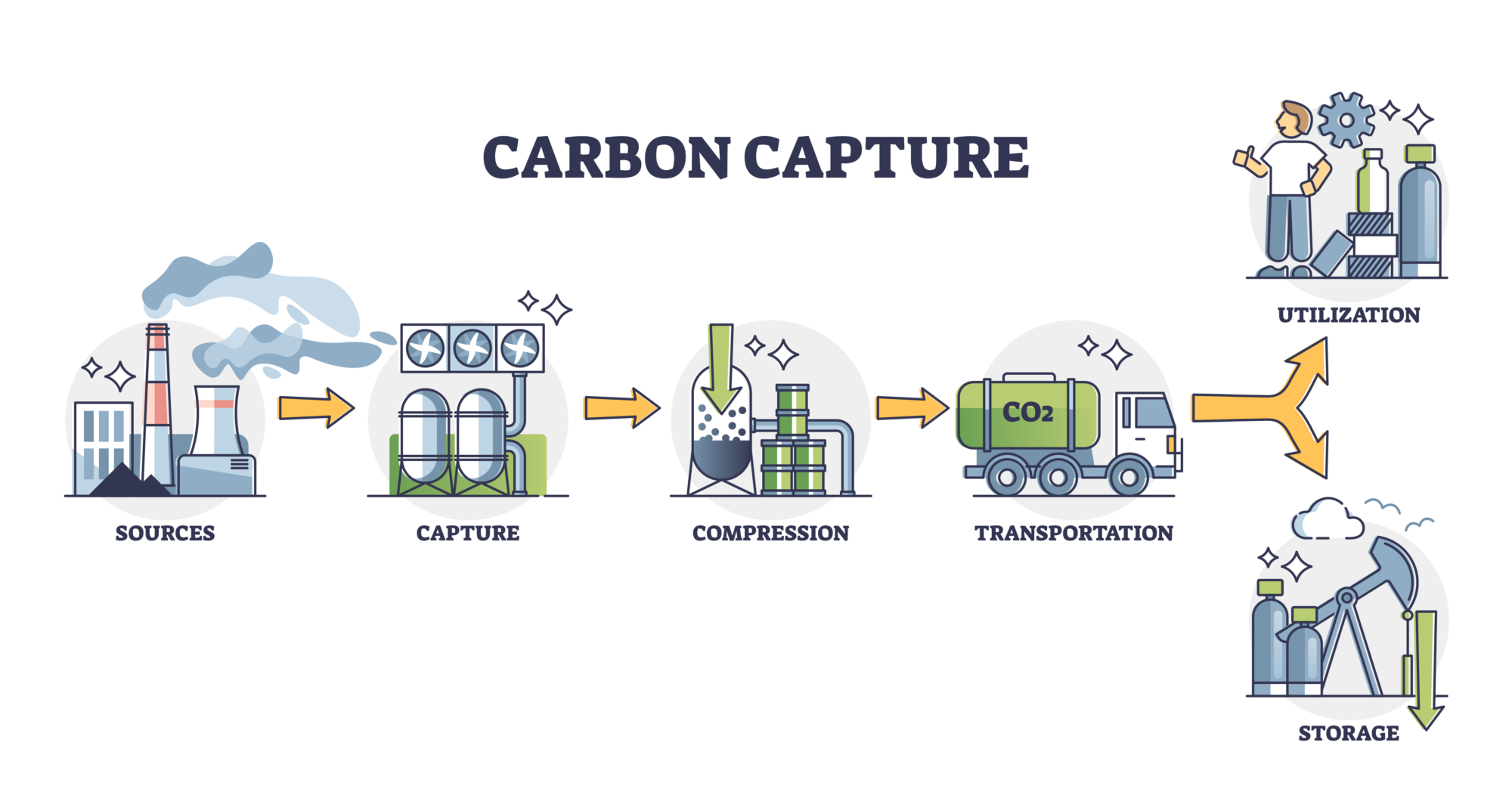
- Capturing CO2 Emissions: Carbon capture involves the collection of CO2 emitted from large-scale industrial facilities, power plants, or even directly from the atmosphere. Several techniques are employed to capture CO2 at its source, ranging from chemical absorption to physical separation and adsorption processes.
- Post-Combustion Capture: In the case of fossil fuel power plants, post-combustion capture is a widely used method. It involves removing CO2 from flue gases after the fuel is burned. This process often utilizes solvents or sorbents to chemically react with CO2, separating it from the exhaust gases.
- Pre-Combustion Capture: For facilities using fossil fuels in a gasification process, such as coal or natural gas, pre-combustion capture is employed. Here, the fuel is transformed into a gas mixture containing hydrogen and carbon monoxide, commonly known as syngas. CO2 is then captured from the syngas before it undergoes combustion.
- Direct Air Capture (DAC): Direct Air Capture offers an innovative approach to carbon capture by directly removing CO2 from ambient air. Advanced technologies, such as large-scale fans and chemical sorbents, capture CO2 molecules, allowing for its subsequent storage or utilization.
- Transporting and Storing Captured CO2: Once CO2 is captured, it needs to be transported and securely stored to prevent its release into the atmosphere. Common storage methods include injecting CO2 deep underground into geological formations, such as depleted oil and gas reservoirs, saline aquifers, or unmineable coal seams. These geological storage sites provide secure and permanent storage solutions.
The Benefits of Carbon Capture:
- Climate Change Mitigation: By capturing and storage CO2 emissions, carbon capture plays a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas levels, effectively mitigating climate change impacts. It enables us to reach emissions reduction targets while transitioning to cleaner energy sources.
- Carbon capture technology can be integrated into various industries, such as power generation, cement production, and steel manufacturing, enabling them to significantly reduce their carbon footprints. It offers a viable solution for decarbonized sectors that are challenging to electrify or transition to renewable energy sources.
- Transition Facilitation: Carbon capture provides a bridging solution during the transition to a low-carbon economy. By allowing existing infrastructure to continue operating with reduced emissions, it buys time for the development and scaling of renewable energy technologies.
- Carbon utilization: Captured CO2 can be put to productive use, such as enhanced oil recovery (EOR) or the production of synthetic fuels, chemicals, and building materials. These applications not only reduce emissions but also create economic opportunities and promote circularity in the carbon value chain.
Carbon capture represents a critical tool in our efforts to combat climate change, offering a pathway to reduce emissions while we transition to a cleaner and sustainable energy future. Continued research, development, and deployment of this technology are essential for realizing its full potential and ensuring a greener world for generations to come.